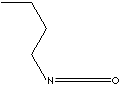
| n-BUTYL ISOCYANATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 111-36-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-862-8 | |
| FORMULA | C4H9NCO | |
| MOL WT. | 99.13 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2929.10 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 600 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 1-Isocyanatobutane; Butyl Isocyanate; | |
| Isocyanic acid butyl ester; n-Butylisocyanat (Dutch); n-Butilo isocianato (Spanish); Isocianato de butilo (Spanish); Isocyanate de butyle (French); | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | -75 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 115 - 116 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.880- 0.890 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Hydrolyses | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 2 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 17 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
Cyanic acid
(the isomer of fulminic acid) is an unstable (explosive), poisonous, volatile,
clear liquid with the structure of H-O-C≡N (the oxoacid formed from the
pseudohalogen cyanide), which is readily converted to
cyamelide and fulminic
acid. There is another isomeric cyanic acid with the
structure of H-N=C=O, called isocyanic acid. Cyanate group (and isocyanate group) can react with itself.
Cyanuric acid (also called pyrolithic acid), white monoclinic crystal with
the structure of [HOC(NCOH)2N], is the trimer
of cyanic acid. The
trimer
of isocyanic acid
is called biuret.
Cyanic acid hydrolyses to ammonia and carbon dioxide in water. The salts and esters of cyanic acid are cyanates. But esters of normal cyanic acid are not known. The salts and esters of isocyanic acid are isocyanates. The isocyanate group reacts with the hydroxyl functional group to form a urethane linkage. Diisocyanates (or polyisocyanates) are monomers for polyurethane production. Polyurethane is made from a variety of diisocyanates in conjunction with polyether and polyester polyols as co-reactants by addition polymerization which needs at least two -N=C=O groups. Polyurethanes are widely used in the manufacture of flexible and rigid foams, fibres, coatings, and elastomers. If isocyanate monomer is polymerized with amine group, polyurea is produced. Cyanates (or Isocyanates) are readily reacts with various form of amine (including ammonia, primary-, secondary-amines, amides and ureas) and hydroxyl functional group. They are used in the synthesis for the target molecules such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, textile softener, lubricants and industrial disinfectants. They can convert to polycyclic compounds such as hydantoins and imidazolons. They are used as plastic additives and as heat treatment salt formulations for metals. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
| ASSAY | 98.0% min | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.880 - 0.890 | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 180kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: I) | |
| UN NO. | 2485 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: F T+, Risk Phrases: 11-14-26-34-37-42, Safety Phrases: 23.2-26-36/37/39-45 | ||